We've compiled a useful list which will define many of the key terms, acronyms and jargon around growth hacking.
While growth hacking uses many of the same tools and techniques used in marketing in general, it has its own approach, and its own vocabulary.
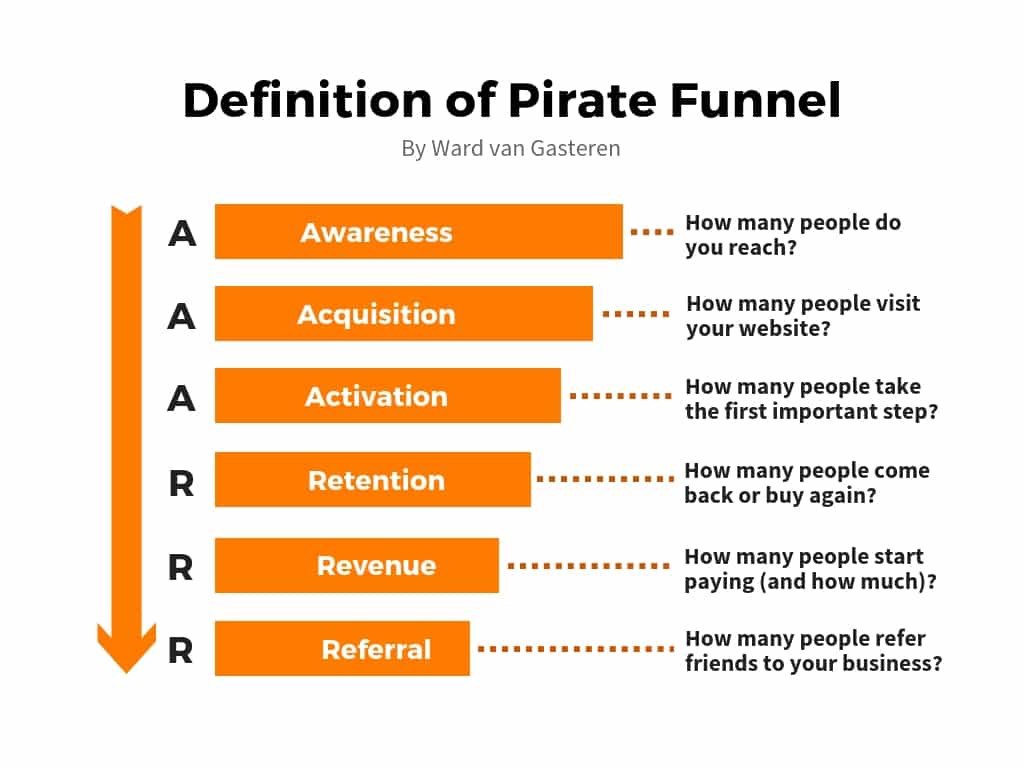
AAARRR
This acronym stands for Awareness, Acquisition, Activation, Revenue, Retention, and Referral. This is the 'pirate metrics' framework created by Dave McClure which is the stages of the growth hacking funnel.
There's an extra 'A' in the latest version, which is the addition of the 'awareness' stage.
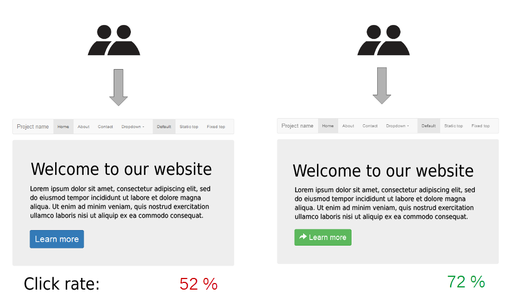
A/B Testing
This is a technique to find the best performing email, landing page, advert etc. of two choices. A/B testing works by splitting your inbound traffic equally between two versions of the same page, or by splitting up your email list to send different variants to subscribers.
It's a great way to find the email or page which achieves your conversion goals, and to make decisions and marketing and design using evidence.
Acquisition
When you attract a user to your site and/or they have has given you some way to identify them, perhaps the submission of an email address.
Acquisition Channel
The channels you are using to acquire customers e.g. email or search. Growth hackers choose target channels carefully to target resources on the channels most likely to deliver growth.
Activation
Encouraging customers to take certain actions, such as purchases or interacting with your site and content. An activated customer is one who hasn't simply converted, but who sees the value of your product and is more likely to become a regular customer.
Agile
Agile is a method of working which relates closely to growth hacking. It is basically about working smarter, rapid iterations, small experiments instead of big bets, frequent empirical feedback and being adaptable to change.
Agile is at the heart of tech working and can drive productivity, improve communication and prioritisation, and ultimately help you to deliver a better customer experience.
Awareness
This is the stage where you are focusing on increasing knowledge of your product or service by your target audience.
Backlog
Experimentation is a key part of growth hacking, but experiments need to be prioritised according to their potential impact.
The backlog is where growth hacking ideas are stored, waiting to be executed, perhaps through a shared document or a dashboard.
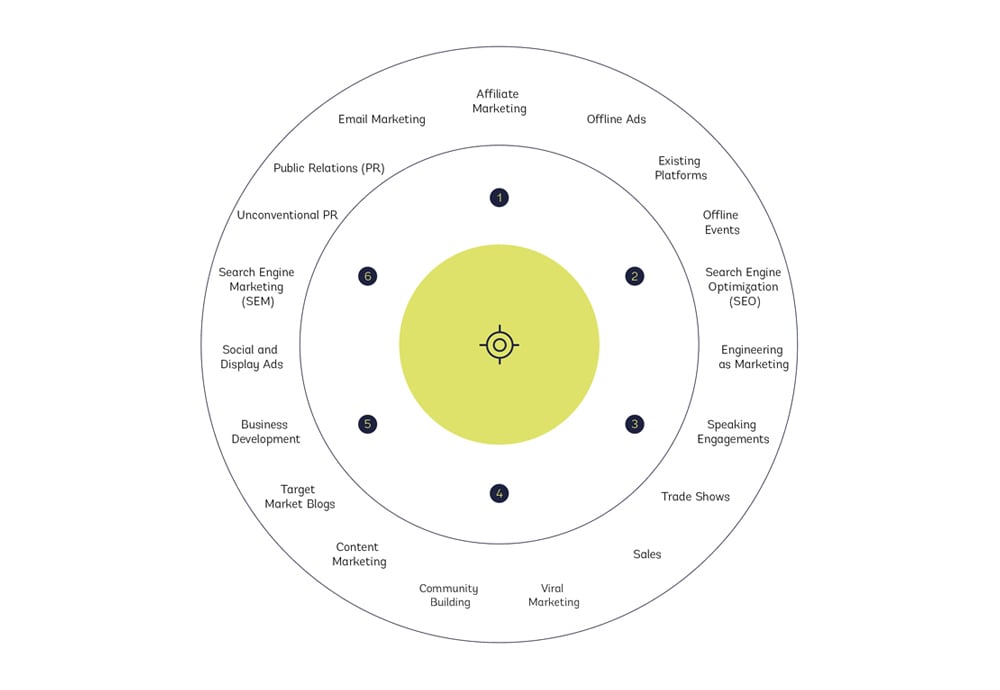
Bullseye Framework
Created by Gabriel Weinberg, this is a simple, but effective process to help growth teams to focus in on the right channels for acquisition.
In this way, efforts and resources can be targeted where they are most likely to be effective.
Churn rate
This is the percentage of customers you lose within a specified time frame. It’s vital to monitor churn, as a high or increasing churn rate is an indication that activation and retention efforts are not as successful as they could be, and it can undermine your growth strategy.
Cohort Analysis
The process of grouping users together based on shared actions and behaviour. This is a retention strategy which better allows marketers to target these groups more effectively. For example, this may be used to identify groups at risk of churn.
Cost per Click
The cost of advertising (e.g., PPC) divided by the number of unique clicks on the ad.
Conversion Rate Optimisation (CRO)
A group of tactics used to increase the number of conversions, such as A/B testing, user testing, and copy optimisation
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
CAC (Customer Acquisition Cost) is a measure of how much you have spent to attract an order from a new customer.
It can be measured by taking the amount you spend on marketing, whether this is PPC, email or other channels, and dividing this figure by the number of new customers that place an order.
Customer lifetime value (CLV)
This is the metric that calculates total revenue we can reasonably expect from a customer throughout the business relationship. The metric considers a customer's revenue value multiplied by our predicted customer lifespan.
Dashboard
A graphical interface showing key metrics and performance which is useful for measuring and sharing progress towards targets.
Events
In analytics, an event an instance of a user taking an action, perhaps clicking a link or loading a page.
Friction
Friction in the funnel caused by usability issues or lack of communication can adversely affect conversion or retention rates.
Growth Experiments
Tests taken to drive increased growth, perhaps by making improvements to the customer journey such as optimising landing pages. Growth experiments are the fuel which drive overall growth hacking efforts.
Growth Levers
These are the mechanisms for influencing growth, the stages of the growth funnel:
- Awareness
- Acquisition
- Activation
- Retention
- Revenue
- Referral
Growth Loops
Created by Brian Balfour, growth loops are closed systems where the inputs generate more of an output that can be reinvested in the input. For example, existing customers helping to acquire new customers through referrals and recommendations.
Growth Mindset
Successful growth hacking requires the right mindset. To quote Sean Ellis, this needs to be people 'whose true north is growth'. The growth mindset is about that focus on growth, and the willingness to be creative and experiment to achieve these goals.
More broadly, it can be a mindset within a company, in which employees are empowered to experiment and take risks in order to achieve growth.
Growth Teams
These are cross-functional teams, often working across the whole funnel. These teams are mandated to take actions to drive growth, and growth teams bring together people with a range of skills and expertise to conduct data analysis, implement changes in the design, functionality, or marketing.
Goal
In analytics, a goal is an action you want users to take on your site or app. This might be a conversion such as a purchase, demo booking or form completion.
ICE
A method of ranking experiment ideas based on their potential impact, how confident you are that it would be successful, and how easy it is to launch it.
Ideas are prioritised according to three criteria, with a score given for each:
- Impact
- Confidence
- Ease
KPI
A measure of performance towards a specific objective.
Language / Market Fit
How effectively the language you use to describe and market your product resonates with your target customer.
Lifetime Customer Value (LTV)
The total amount of revenue earned from a customer over the life of the business relationship with them.
Marketing Funnel
An illustration of the journey that your customers take towards the purchase of your product or service.
Metrics
Metrics are used to track, monitor, and assess the success or failure of campaigns or business processes.
As only things that are measured can be effectively improved, metrics matter.
North Star Metric
The north star metric is the one metric that captures the core value that your product delivers to customers. Optimising for this metric is key to driving sustainable business growth.
Examples of north star metrics include:
- Airbnb - number of bookings
- Lyft - number of rides
- Shopify - number of active merchants
Or Objectives & Key Results. The objective is what you want to do, and the deadline for achieving it. Key Results are the benchmarks you can measure that track your progress toward the Objective.
OKR is a tool that helps teams align the goals of the individual with the goals of the team and the company.
OMTM
One Metric That Matters (OMTM) is an ambitious growth goal set by a business that guides all of a growth hacker’s activities. It should be tied to the North Star Metric.
It should be ambitious, measurable, achievable and specific. For example, a company might have a 2-year target related to revenue or user numbers.
Persona
A semi-fictional representation of a type of customer based on market research that can be used to guide marketing efforts.
PIE framework
This is a variation on the ICE framework for prioritising growth experiments. It considers three factors:
- Potential - how likely is it to succeed?
- Importance - how valuable could it be?
- Ease - how difficult or costly is this experiment?
As with ICE, experiment ideas are scored and prioritised according to each criteria.
Product Market Fit
For growth hackers, product market fit is considered the foundation for business growth. It means that your product offerings and your target audience’s expectations are perfectly in sync.
Essentially, it means you have a product that people want to buy and use. It's the basis for a successful growth strategy.
Referral
The last stage of the Pirate Funnel. Referral happens when customers value your product enough to refer it to others, attracting more potential customers to your brand.
Referral strategies include affiliate programs, rewards for customer referrals, and more.
Retention
Retention is another stage of the growth hacking (pirate) funnel. It refers to how many people are coming back to your product or buying from you again.
Many companies place more focus on acquisition, but it's important to consider retention, as this holds the potential for more sustainable long-term growth. As such, it's an important area for growth hackers.
Revenue
Revenue is another growth funnel stage. It relates to strategies such as pricing, cross-selling and upselling which can be used to increase revenues.
Segment
Users who are grouped together on the basis of a shared characteristic. This may be by acquisition channels, demographics, average spend, and more.
Social Proof
Social proof revolves around the instinct to follow the example of others and do what they do. If a restaurant looks busy, we’ll take that as a sign the food’s good.
In marketing, user reviews and recommendations, social posts about products, and features such as customer testimonials are all persuasive forms of social proof.
Sprints
A set period in which a growth team works to complete a specific collection of experiments and deliverables.
T-shaped model
Growth hackers need a breadth and depth of knowledge and skills within all different fields of marketing. The top of the T represents the breadth of knowledge, while the vertical line represents the depth, or specialist skills required.

Triggers (in Growth Hacking)
Actions used to influence customer behaviour, to trigger a response from customers. This could be mobile app alerts or cart abandonment emails for example.
User Experience (UX)
The ease or difficulty with which a user can complete tasks or action on a web page, app etc. In general, the better the UX, the more likely customers will download content or make a purchase.
UX is a key focus for growth hackers as eliminating areas of friction can improve conversion rates and customer satisfaction.
